Chair of Optoelectronics, Prof. Dr. Karl-Heinz Brenner (Emeritus)
Status
After 22 years as head of the Chair of Optoelectronics, Prof. Dr. Karl-Heinz Brenner retired in April 2018. However, he is still active in the field of optics.
History and Research
The Chair of Optoelectronics began its work at the university of Mannheim in the spring of 1996 as one of the first chairs of the newly founded Institute of Computer Engineering. In 2008, the Institute with all its components was transferred from Mannheim to the university of Heidelberg. The research activities of the Department of Optoelectronics covered the development of optics simulation algorithms, reaching from scalar optics to rigorous electromagnetic methods. The design and fabrication of non-imaging optical components was another research area of the chair. Non-imaging elements were used for beam shaping of edge-emitting semiconductor lasers and for the illumination of optical systems. Furthermore, the research concentrated on the optimization, fabrication and characterization of micro-optical components and systems. The main application areas of these components are in optical communication and in sensors.
Selected Research Examples
|
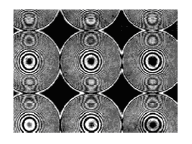
High performance microlenses by field assisted ion exchange in glass (SMOS)
Planar microlenses with high focal power and diffraction-limited performance were realised with field assisted ion exchange in glass. By considering proximity effects between the charged ions, a wide range of phase distributions can be also be obtained. |
|
|
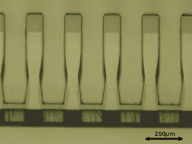
Light deflecting optical elements by deep lithography
Optical interconnects offer the possibility to increase the bandwidth on the chip to chip or board to board level significantly. For the coupling between source/detector and fibres, opto-mechanical components with a deflection angle of 90° are required. Deep lithography in thick resists is a suitable method to produce structures in the order of a few 100µm with an accuracy of better than 2µm. 45° mirror elements were achieved by slanted exposure. |
|
|
Two-dimensional beam shaping of semiconductor lasers
With the Gaussian-elliptic emission profile of edge-emitting semiconductor lasers, much light is wasted at the collimation lens. By shaping this intensity profile, the efficiency can be significantly improved. While the theory of one-dimensional or rotationally symmetric transformations is well understood, the theory for two-dimensional transformers is much more demanding. We developed a 2D-method to design beam shaping elements for edge emitting semiconductor lasers. Thus the elliptic Gaussian beam profile is converted to a homogeneous, rotationally symmetric beam with almost 95% efficiency. |
|


|
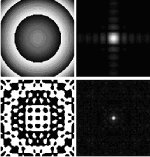
Diffractive micro lens arrays with overlapping apertures
Diffractive micro lens arrays offer a fundamental advantage over refractive ones: the effective numeric aperture (NA) can be selected independent of the lens pitch and the focal length.. The effective NA is given by the diameter of the pupil. If the effective NA is larger than the cell NA, an overlapping micro lens array is realized. By lens overlapping, a dense array with large working distance and high numerical aperture is possible. |
|
|
Construction of a Plenoptic Camera
A plenoptic camera consists of a micro lens array (MLA), which is positioned in the image plane of a classic imaging system. The image sensor is located one micro lens focal length behind the MLA. The MLA pitch is usually chosen such that one micro lens covers approximately 10-20 sensor pixels in one dimension. Furthermore, the camera sensor ideally has a high resolution. Moreover, an objective lens with small focal length and small sensor pixels are advantageous for a later wave-optical simulation / reconstruction. Our setup uses an AVT Guppy F-503 industrial camera with a 5 megapixel CMOS sensor and 2.2µm pixel pitch. A MLA (circular lenses on a quadratic grid) with 110µm pitch and 0.03 numerical aperture manufactured by Süss MicroOptics is employed. We use a Tamron 25mm C-mount objective lens with adjustable aperture size. This is necessary to ensure that individual micro lens images do not overlap. |
|

|
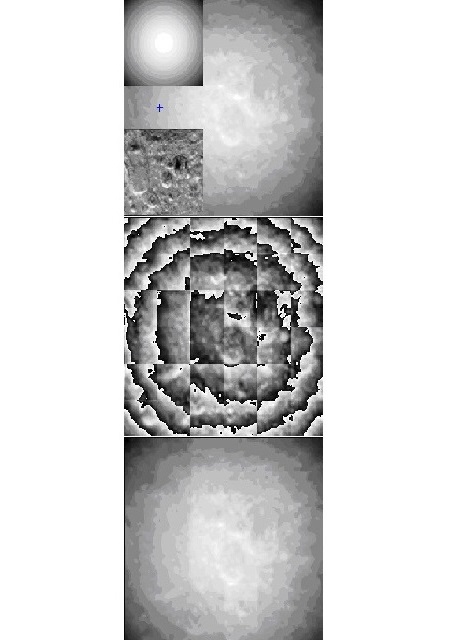
Sensitivity-enhanced phase retrieval with multi-plane intensity detection and a micro lens array
Phase retrieval methods like the classical Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm have an advantage compared to interferometric and holographic methods, in that they require no reference wave. Thus no laser is required and the set-up can be very simple and stable. Multi-plane methods obtain the complex amplitude from a sequence of diffraction intensities, but this method cannot handle smooth phase distributions. There, the intensity change along the propagation direction z is too small for a reliable reconstruction. Here we propose an extension of his method by including a micro lens array, similar to a Hartmann-Shack-sensor (HS). The array enhances the intensity variation of the recorded intensity patterns and, because it is known, it is numerically easy to eliminate it from the recovered phase distribution. |
|
|
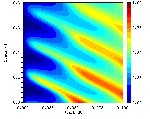
Two and three-dimensional Rigorous Coupled Wave Analysis
The rigorous coupled wave analysis is an advanced theory for the calculation of exact electromagnetic near-field distribution and in particular for the analysis of diffraction gratings. At our chair we have developed two powerful simulation environments to study resonant effects in one and two-dimensional diffraction gratings. Especially the two-dimensional case, which leads to three-dimensional fields, can require big amounts of memory and CPU time. This is why we developed a variety of enhancements to reduce both, calculation time and memory consumption. We also developed a theory to calculate the local absorption inside a structure, enabling us to optimize detector layouts. |
|
|
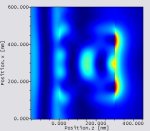
Optimization of local absorption in layered media
Local absorption plays an important role in all semiconductor detectors and solar cells. Since all the standard theories only provide global absorption, being defined as the difference of incoming power and the sum of reflected and transmitted power, no information about the position within the stack where absorption takes place is available. In semiconductors, the photon to electron conversion is most efficient, if the absorption takes place at or near the depletion layer, while absorption at other positions only contributes to heat generation. Being able to compute local absorption, an optimization with respect to conversion efficiency becomes possible. |
|
|
Publications
In the following, all works published by Prof. Brenner and members of the Chair of Optoelectronics can be found.
Publications:
| |
1980-1989
Details
- H. Bartelt, K.-H. Brenner, A.W. Lohmann: "The Wigner distribution function and its optical production", Opt. Comm. 32, No.1, 32 - 38, (1980)
- H. Bartelt, K.-H. Brenner, "The Wigner Distribution Function: An Alternate Signal Representation in Optics", Israel Journal of Technology, Vol. 18, 260 - 262, (1980)
- H. Bartelt, K.-H. Brenner, "The Wigner Distribution Function - Experiments and Applications", AIP Conf. Proc. No. 65, Subseries on Optical Science and Engineering No. 1, "Optics in Four Dimensions - 1980", (ICO, Ensenada) ed. M.A. Machado, L.M Narducci, 332 - 339, New York (1981)
- K.-H. Brenner, A.W. Lohmann: "Wigner distribution function display of complex 1D signals", Opt. Comm. 42, No. 5, 310 - 314, (1982)
- K.-H. Brenner, K. Wodkiewicz: "Time dependent physical spectrum of light and the Wigner distribution function", Opt. Comm. 43, No. 2, 103 - 106, (1982)
- K.-H. Brenner, A.W. Lohmann, J. Ojeda-Castaneda: "The ambiguity function as a polar display of the OTF", Opt. Comm. 44, No. 5, 323 - 326, (1983)
- K.-H. Brenner, A.W. Lohmann, J. Ojeda-Castaneda: "Lau effect: OTF theory", Opt. Comm. 46, No. 1, 14 - 16, (1983)
- K.-H. Brenner: "A discrete version of the Wigner distribution function", in Proceedings of the 2nd European Signal Processing Conf., EUSIPCO 1983, Erlangen, Germany, Sept. 1983, H.W. Schüssler (editor), Elsevier Science Publishers B.V, 307 - 310, Eurasip, North-Holland (1983)
- K.-H. Brenner, J. Ojeda-Castaneda: "Ambiguity function and Wigner distribution function applied to partially coherent imagery", Optica Acta 31, No. 2, 213 - 223, (1984)
- Brenner Karl-Heinz; and Huang, Alan; "Optical implementations of symbolic substitution (A)" J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1, pp 1292 (1984)
- Brenner Karl-Heinz; and Huang, Alan; "Logic and architectures for digital optical computers (A)" J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 3, P 62 (1986)
- K.-H.Brenner, A. Huang, N. Streibl: "Digital Optical Computing with Symbolic Substitution", Appl. Opt. 25, No. 18, 3054 - 3060, (1986)
- Brenner Karl-Heinz; "New implementation of symbolic substitution logic" Appl. Opt. 25, No. 18, 3061 - 3064, (1986)
- K. -H. Brenner, A. W. Lohmann, “The digital optical computing program at Erlangen”, in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of CONPAR 86, Springer Berlin / Heidelberg, Volume 237/1986, p. 69-75 (1986)
- Brenner, K.-H. Lohmann, A.”Optical circuitry and architectures for digital optical computing” Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, IEEE International Conference on ICASSP '86., Volume: 11, p. 477 – 480 (1986)
- J. N. Mait and K. -H. Brenner, "Dual-phase holograms: improved design," Appl. Opt. 26, 4883-4892 (1987)
- K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang: "Optical Implementations of the Perfect Shuffle Interconnection", Appl. Opt. 27, No. 1, 135 - 137, (1988)
- K.-H. Brenner, K.-H.: "Digitale optische Computer", Laser Magazin Nr. 3, 30, (1988)
- K.-H. Brenner, J.N. Mait: "Optical symbolic substitution: System design using phase-only holograms", Appl. Opt. 27, No. 9, 1692 - 1700, (1988)
- K.-H. Brenner, A.W. Lohmann: "Cyclic shifting for optical data processing", Appl. Opt. 27, No.3, 434 - 436, (1988)
- K.-H. Brenner: "Programmable optical processor based on symbolic substitution", Appl. Opt. 27, No. 9, 1687 - 1691, (1988)
- Invited: K.-H. Brenner: "Digital Optical Computing", Appl. Phys. B 46, 111 - 120, (1988)
- K.-H. Brenner, F. Sauer: "Diffractive-Reflective optical interconnects", Appl. Opt. 27, No. 20, 4251 - 4254, (1988)
- K.-H. Brenner, A.W. Lohmann, T. Merklein: "Symbolic Substitution implemented with spatial filtering", Opt. Eng. 28, No 4, 390 - 395, (1989)
- N. Streibl, K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, J. Jahns, J. Jewell, A. Lohmann, D. Miller, M. Murdocca, M.E. Prise, Th. Sizer: "Digital Optics", Proc. IEEE 77, Vol. 77, No 12, 1954 - 1969, (1989)
1990-1999
Details
- P.B. Berra, K.-H. Brenner, W.T. Cathey, H.J. Caulfield, S.H. Lee, H.H. Szu: "Optical database/kowledgebase machines", Appl. Opt. 29, No. 2, 195 - 205, (1990)
- K.-H. Brenner, M. Kufner, S. Kufner: "Highly parallel arithmetic for a digital optical processor using symbolic substitution logic", Appl. Opt. 29, No. 11, 1610 - 1618, (1990)
- K.-H. Brenner, M. Frank, M. Kufner, S. Kufner: "H+ lithography for 3D-integration of optical circuits", Appl. Opt. 29, No. 26, 3723 - 3724, (1990)
- K.-H. Brenner, D. Fey: "Digital optical arithmetic based on systolic arrays and symbolic substitution logic", Int. J. of Opt. Computing,Vol. 1, 153 - 169, (1990)
- Gary E. Lohmann and Karl-Heinz Brenner, “Morphological optical image processor”, Conference “Optics in Complex Systems”, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol 1319, p. 161, Garmisch (1990)
- G.E. Lohmann, K.-H. Brenner: "Digital optical processor based on cellular automata", in "Digital Image Processing and computer graphics theory and applications", E. Wenger, D. Dimitrov eds., Oldenburg Verlag, Schriftenreihe der Österreichischen Computer Gesellschaft (ÖCG), Band 58, ISBN 3-85403-058-1, 152 -172, (1991)
- K.-H. Brenner: "3D-Integration of Digital Optical Systems", in Optical Computing, OSA, Technical Digest Vol. 6, 25 - 28, Salt Lake City Utah, MB2, (1991)
- G.E. Lohman, K.-H. Brenner: "Optical Morphological Image Processor", in Optical Computing, OSA, Technical Digest Vol. 6, 220 - 222, Salt Lake City Utah, TuB4, (1991)
- K.-H. Brenner: "Three-dimensional integration of optical systems", in SPIE Proceedings, Vol. 1506, Micro-Optics II, 94 - 98, The Hague (1991)
- K.-H. Brenner: "Techniques for integrating 3D-optical systems", in Miniature and Micro-Optics, San Diego,SPIE Proceedings 1544, 263 - 270, (1991)
- H. Rajbenbach, S. Bann, P. Refregier, P. Joffre, J.P. Huignard, H.S. Buchkremer, A.S. Jensen, E. Rasmussen, K.-H. Brenner, G.E. Lohman: "Compact photorefractive correlator for robotic applications", Appl. Opt. 31, No 26, 5666 - 5674, (1992)
- K.-H. Brenner, T. M. Merklein: "Implementation of an optical crossbar network based on directional switches", Appl. Opt. 31, No. 14, 2446 - 2451, (1992)
- G.E. Lohman, K.-H. Brenner: "Space-variance in optical computing systems", Optik 89, No. 3, 123 - 134, (1992)
- J. Jahns, K.-H. Brenner, W. Däschner, C. Doubrava, T. Merklein: "Replication of diffractive microoptical elements using a PMMA molding technique", Optik 89, No. 3, 98 - 100, (1992)
- K.-H. Brenner, W. Eckert, S. Kufner, J. Moisel, S. Sinzinger, G. Borghs, M. Kuijk, P. Heremans: "Cascading of two pnpn-photothyristor arrays in a microoptical system: an experimental demonstration", in Diffractive Optics, OSA Technical Digest Vol. 9, 3 - 8, New Orleans (1992)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, J. Moisel, W. Singer, S. Sinzinger, T. Spick, M. Testorf: "Diffusion elements in glass: comparison and optimization of the diffusion response in different substrates", Proceedings of the ICO Topical Meeting on Optical Computing, 234 - 242, Minsk (1992)
- K.-H. Brenner, M. Frank, M. Kufner, S. Kufner, A. Müller: "Deep Proton Irradiation of PMMA for a 3D-integration of microoptical components", in Integrierte Optik und Mikrooptik mit Polymeren, Max-Planck-Institut für Polymerforschung Mainz,160 - 176, (1992)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, J. Moisel, W. Singer, S. Sinzinger, T. Spick and M. Testorf, "Modification of the imaging properties of ion-exchange microlenses by mask shaping", in Technical Digest of the Tenth Topical Meeting on Gradient-Index Optical Systems, (European Optical Society, 1992), p. 187, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 4-6- Oct. 1992
- K.-H. Brenner, „Three dimensional microoptical integration techniques“, in Optical Computing, Spie Proceedings 1806 (Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers, Washington), 98 - 104, Minsk Belarus (1992)
- K.-H. Brenner, M. Kufner, S. Kufner, J. Moisel, A. Müller, S. Sinzinger, M. Testorf, J. Göttert, J. Mohr: "Application of three-dimensional micro-optical components formed by lithography, electroforming, and plastic molding", Appl. Opt. 32, No. 32, 6464 - 6469, (1993)
- K.-H. Brenner: "Digital Optical Computing", (invited) Buchkapitel in "Organic Materials for Photonics", Summerschool on organic materials, Obereggen 1991, ed. G. Zerbi, North Holland Amsterdam (1993)
- G. Bagordo, K.-H. Brenner, T. Merklein, A. Rohrbach: "Fabrication of Micro-Optic Elements by UV-initiated Polymerisation", in "Integrated Optics and Micro-Optics with Polymers", Ehrfeld, Wegner, Karthe, Bauer, Moser editors, Teubner-Texte zur Physik, Band 27, 177 - 192, (1993)
- K.-H. Brenner, M. Frank, M. Kufner, S. Kufner, A. Müller: "Deep Proton Irradiation of PMMA for a 3D-Integration of Micro-Optical Components" in "Integrated Optics and Micro-Optics with Polymers", Ehrfeld, Wegner, Karthe, Bauer, Moser editors, Teubner-Texte zur Physik, Band 27, 159 - 177, (1993)
- S. Kufner, M. Kufner, M. Frank, A. Müller, K.-H. Brenner: "3D-integration of refractive microoptical components by deep proton irradiation", Pure Appl. Opt. 2, 111 - 124, (1993)
- K.-H. Brenner, W. Singer, "Light propagation through microlenses: a new simulation method", Appl. Opt. 32, No. 26, 4984 - 4988, (1993)
- Ozaktas Haldun M.; Brenner, Karl-Heinz; and Lohmann, Adolf W.; "Interpretation of the space-bandwidth product as the entropy of distinct connection patterns in multifacet optical interconnection architectures" J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 10, No. 3, 418 - 422, (1993)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, T. Spick, S. Sinzinger, M. Testorf, "Index-distributed planar microlenses for three-dimensional micro-optics fabricated by silver-sodium ion exchange in BGG35 substrates", Appl. Opt. 33, No. 25, 5919 - 5924, (1994)
- W. Singer, M. Testorf, K.-H. Brenner, "Gradient index microlenses: numerical investigation of different spherical index profiles with the wave propagation method (WPM)", Appl. Opt. 34, No.13, 2165 - 2171, (1994)
- K.-H. Brenner, W. Eckert, C. Passon, „Demonstration of an optical pipeline adder and design concepts for its microintegration“, Optics & Laser Technology 26, No 4, 229 - 237, (1994)
- J. Moisel, K.-H. Brenner, „Demonstration of a 3D integrated refractive microsystem“, in Opt. Comput, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. No 139 / Part II (IOP Publishing Ltd), 259 - 262, Edinburgh (1994)
- S. Sinzinger, K.-H. Brenner, J. Moisel, T. Spick, M. Testorf, "Astigmatic gradient-index elements for laser-diode collimation and beam shaping", Appl. Opt. 34, No. 29, 6626 - 6632, (1995)
- W. Singer, K.-H. Brenner, „Transition of the scalar field at refracting surface in the generalized Kirchhoff-diffracrion theory“, J. Opt. Soc. Am A 12, No. 9, 1913 - 1919, (1995)
- Rohrbach, K.-H. Brenner, „Surface-relief phase structures generated by light- initiated polymerisation“, Appl. Opt. 34, No. 22, 4747 - 4754, (1995)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, „Realization of 0.2-N.A. microlenses by field assisted Ag-Na ion exchange“, European Optical Society (EOS) Topical Meeting on microlens arrays, NPL Teddington, UK, 11.-12. May 1995, (1995)
- W. Singer, B. Dobler, H. Schreiber, K.-H. Brenner, B. Messerschmidt, „Refractive- index measurement of gradient-index microlenses by diffraction tomography“, Appl. Opt. 35, No. 13, 2167 - 2171, (1996)
- C. Passon, J. Moisel, N. McArdle, W. Eckert, K.-H. Brenner, M. Kuijk, P. Heremans, „Integration of refractive micro-optical elements with differential-pair optical-thyristor arrays“, Appl. Opt. 35, No. 8, 1205 - 1211, (1996)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, „Realization and optimization of planar refracting microlenses by Ag-Na ion-exchange techniques“, Appl. Opt. 35, No. 25, 5102 - 5107, (1996)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, „Iterative reconstruction of a gradient index distribution from one interferometric measurement“, OPTIK 102, No. 3, 101 - 105, (1996)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, „Optimization of planar microlenses by Ag-Na ion exchange techniques“, in Optical Computing, JSAP (The Japan Society of Applied Physics), Technical Digest 1, 234 - 242, Sendai, Japan (1996)
- Kirk, A. Goulet, H. Thienpont, N. McArdle, K.-H- Brenner, M. Kuijk, P. Heremans, I. Veretennicoff, „Compact optical imaging system for arrays of optical thyristors“, Appl. Opt., 36, No. 14, 3070 - 3078, (1997)
- J. Moisel, C. Passon, J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, „Homogeneous concept for the coupling of active and passive single-mode devices utilizing planar gradient-index lenses and silicon-V-grooves“, Appl. Opt. 36, No. 20, 4736 - 4743, (1997)
- K.-H. Brenner, U. Krackhardt, „Perspektiven optischer Übertragungs- undVerarbeitungssysteme vor dem Hintergrund einer stetigen Leistungssteigerung in der Digitalelektronik“, in ARCS ´97 (Architektur von Rechensystemen), ed. R. Hoffmann, B. Klauer, Ch. Müller-Schloer u. a., ISBN 3-86009-121-2, 141 - 153, Rostock (1997)
- K.-H. Brenner, J. Bähr, “GRIN-Microoptical components in communication and computing”, in MOC/Grin ’97, JSAP, Technical Digest AP971222, 24 - 27, Tokio (1997)
- W. Singer, K.-H. Brenner "Stacked Micro-optical Systems" in Micro-optics, Elements, systems and applications, ed. H.P. Herzig, Taylor & Francis Ltd. London, p. 199 - 221, ISBN 0-7484-0481-3 (1997)
- D. Dragoman, K.-H. Brenner; M. Dragoman, J. Bähr, U. Krackhardt, „Hemispherical-rod microlens as a variant fractional Fourier transformer“, Opt. Lett., 23, No 19, 1499 - 1501, (1998)
- Karl-Heinz Brenner, "Technologies for Realizing Dynamically Reconfigurable Optical Interconnections", in Dagstuhl-Seminar-Report 201 („Dynamically Reconfigurable Architectures“), No. 98081, page 9 - 10, (1998)
- R. Klug, U. W. Krackhardt, K.-H. Brenner, "Richtungsmultiplex für optische Verbindungen zwischen Platinen", Tagungsbeitrag ORT, C- LAB. Paderborn, (1998)
- K.-H. Brenner, R. Klug, A. Knüttel, "Microoptic Implementation of an Array of 1024 Confocal Sensors", in OPTO '98 Proceedings, AMA Fachverband für Sensorik,155 -160, Erfurt (1998)
- K.-H. Brenner, U.W. Krackhardt, R. Klug, "Directional Multiplexing for optical Board to Board Interconnections", in Optics in Computing '98, Proceedings of SPIE 3490, 416 - 418, Bruegge (1998)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, "Optical motherboard: a planar chip to chip interconnection scheme for dense optical wiring", in Optics in Computing '98, Proceedings of SPIE 3490, 419 - 422, Bruegge (1998)
- R. Klug, U.W. Krackhardt and K.-H. Brenner, , "Directional Multiplexing for optical Board to Board Interconnections", OPTIKA 98, 14 - 17.09.98, Budapest, Ungarn, Proceedings of SPIE 3573, (1998)
- K.-H. Brenner, U. Krackhardt, "Komponenten und Aufbautechniken für mikro-optischeSysteme zur Informationsübertragung", it+ti 41, Nr. 6, 39 - 48, (1999)
- D. Dragoman, M. Dragoman, J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, "Phase space measurements of micro-optical objects", Appl. Opt. 38, No 23, 5019 - 5023, (1999)
- R. Klug, U. W. Krackhardt, K.-H. Brenner, "Angular Multiplexing for optical Board to Board Interconnections",in Optics in Computing, OSA Technical Digest, 118 - 120, Snowmass (1999)
- Ulrich Krackhardt, K.-H. Brenner, "The Berry-Phase applied to optical Metrology", in Proceedings of the Workshop on Physics and Computer Science (Editor: Werner Kluge, Department of Computer Science, Christian-Albrechts-University Kiel), 177 - 185, Heidelberg (1999)
- D. Dragoman, M. Dragoman, K.-H. Brenner, "Experimental demonstration of a continuously variant fractional Fourier transformer". Appl. Opt. 38, No. 23, 4985 - 4989, (1999)
- R. Klug, K.-H. Brenner, "Implementation of multilens micro-optical systems with large numerical aperture by stacking of microlenses", Appl. Opt. 38, No. 34, 7002 - 7008, (1999)
- D. Dragoman, M. Dragoman, K.-H. Brenner, "Variant fractional Fourier transformer for optical pulses", Opt. Lett. 24, No. 14, 933 - 935, (1999)
- K.-H. Brenner, R. Klug, U.W. Krackhardt, "Angle division multiplexing in multi-mode fibers for optical board-to-board interconnection", SPIE, Vol. CR74, eds P. Réfrégier, B. Javidi, Euro-American Workshop on Optoelectronic Information Processing, Critical Review, 61 - 69, (1999)
- K.-H. Brenner, "Analysis of phase anomalies and design of continuous phase elements", in Diffractive Optics '99, EOS Topical Meeting Digest Series 22, ISSN 1167-5357, 22 - 23, Jena (1999)
- U. W. Krackhardt, K.-H. Brenner, "Forward Construction of HOEs by Continuous Aperture Division", in Diffractive Optics '99, EOS Topical Meeting Digest Series 22, ISSN 1167-5357, 163 - 164, Jena (1999)
- U. W. Krackhardt, R. Klug, K.-H. Brenner, "Faser-optische Kurzstreckenverbindungen zur breitbandigen und parallelen Signalübertragung", ORT 1999, Tagungsband 4. Workshop Optik in der Rechentechnik, ISSN 1437-8507, 10 - 15, Jena (1999)
2000-2009
Details
- U.-W. Krackhardt, R. Klug, K.-H. Brenner, "Broadband parallel fiber optical link for short distance interconnection with multi-mode fibers", Appl. Opt. 39, No. 5, 690 - 697, (2000)
- K.-H. Brenner, "Method for designing arbitrary two-dimensional continuous phase elements", Opt. Lett. 25, No. 1, 31 - 33, (2000)
- U. W. Krackhardt, R. Klug, K.-H. Brenner, "Demonstration of a parallel optical transmission using angle multiplexing in optical fibres", Optics in Computing 2000, Roger A. Lessard, Tigran Galstian, Editors, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 4089, 86 - 92, ISBN 0-8194-3732-8, ISSN 0277-786X, Quebec City, Canada (2000)
- K.-H. Brenner, J. Bähr, T. Schmelcher, "Design and Fabrication of arbitrary , non-separable continuous phase elements", in Diffractiv Optics and Micro-Optics, OSA Technical Digest, 237 - 239, ISBN 1-55752-635-4, Quebec City, Canada (2000)
- U. W. Krackhardt, R. Klug, and K.-H. Brenner, "Multimode Fiber Interconnect for Parallel, High Bandwidth - Short Distance Data Link, in Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), The Electromagnetics Academy, PIERS 2000 Proceedings, 726, ISBN 0-9679674-0-6, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA (2000)
- Daniela Dragoman, Mircea Dragoman, and Karl-Heinz Brenner, "Optical realization of the ambiguity function of real two-dimensional light sources", Applied Optics 39, No. 17, 2912 - 2917, (2000)
- INVITED: Karl-Heinz Brenner, "Development of modules for micro optical integration and MOEMS packaging", in MOEMS and Miniaturized Systems, Eds: M. Edward Motamedi, Rolf Göring, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 4178, 138 - 140, ISSN 0277-786X, Santa Clara, USA (2000)
- P. Kümmel, U. Krackhardt, K.-H. Brenner, S. Dambach, "Berechnung und Herstellung mikrooptischer Elemente für den blauen DVD-Standard", 5. Workshop Optik in der Rechentechnik, Tagungsband, eds.: Stefan Sinzinger, Jürgen Jahns, 69 - 73, ISSN 1437-8507, Hagen (2000)
- U. W. Krackhardt, R. Klug, K.-H. Brenner, "Realistion and Application of a parallel high-bandwidth Interconnect over a single multimode Fibre by Angle Division Multiplexing", in 14th International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, A.G. Mignani, H.C. Lefèvre, Editors, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 4185, 174 - 177, ISSN 0277-786X, Venedig (2000)
- J. Bähr, T. Schmelcher, K.-H. Brenner, "Tolerant Coupling of integrated Multimode Waveguides", in LEOS 2000, IEEE Annual Meeting Conference Proceedings, Vol. 2, 571 - 572, ISBN 0-7803-5947-X, Puerto Rico (2000)
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, "H-ROD: A new and versatile microoptical component", OPTIK 112, No 7, 289 – 294, (2001)
- Jochen Bähr, Thilo Schmelcher, Karl-Heinz Brenner, "Tolerant Coupling of integrated Multimode Waveguides", in Optics in Computing, OSA Technical Digest, 116 – 118, ISBN 1-55752-656-7, Lake Tahoe/Nevada (2001)
- U. Krackhardt, R. Klug, K.-H. Brenner, "Angle Division Multiplexing: Investigation of the multiplexing potential of real systems", ORT 2001, Proceedings 6th Workshop Optics in Computing Technology, 101 – 108, ISSN 1437-8507, Paderborn (2001)
- T. Schmelcher, J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner "Tolerant Coupling of integrated Multimode Waveguides", ORT 2001, Proceedings 6th Workshop Optics in Computing Technology, ISSN 1437-8507, 87 – 91, Paderborn (2001)
- Ulrich Krackhardt, Karl-Heinz Brenner, „Integrated Guiding Structures for automatic Alignment of micro optical Components“, SPIE 46. Annual Meeting, Gradient Index, Miniature, and Diffractive Optical Systems II, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 4437, 91 – 98, ISSN 0277-786X/01, San Diego (2001)
- Jochen Bähr, Karl-Heinz Brenner, „Realization of refractive continuous phase elements with high design freedom by mask structured ion exchange“, SPIE 46. Annual Meeting, Gradient Index, Miniature, and Diffractive Optical Systems II, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 4437, 50 – 60, ISSN 0277-786X/01, San Diego (2001)
- Karl-Heinz Brenner, Peter Kümmel, Uwe Zeitner, „Design, analysis and fabrication of refractive beam shaping elements for optical storage applications“, SPIE 46. Annual Meeting, Laser Beam Shaping II, Poceedings of SPIE, Vol. 4443, 93 – 104, ISBN 0-8194-4157-0, San Diego, USA (2001)
- Invited: Karl-Heinz Brenner, „Image formation by beam shaping. Design methods and applications“, Workshop Optics for Information Systems, 4th Euro-American Workshop, Optoelectronic Information Processing: Optics for Information Systems, Critical Reviews of Optical Science and Technology, Vol. CR81, 1 – 12, ISBN 0-8194-4123-6, Valencia, Spain (2001)
- INVITED: J. Bähr, U. Krackhardt, K.-H. Brenner „Fabrication and Testing of planar Micro Lens Arrays by Ion Exchange Technique in Glass“, in Proceedings of SPIE, Micro- and Nano-optics for Optical Interconnection and Information Processing, eds. M.R. Taghizadeh, H. Thienpont, G.E. Jabbour, Vol. 4455, pp.281 – 292, SPIE 46. Annual Meeting, San Diego, USA (2001)
- D. Dragoman, M. Dragoman, K.-H. Brenner " Tomographic amplitude and phase recovery of vertical-cavity surface emitting lasers using the ambiguity function", Optics Letters. Vol. 27, No. 17, 1519 – 1521, ISSN 0146-9592 (2002)
- Daniela Dragoman, Mircea Dragoman, and Karl-Heinz Brenner, "Amplitude and phase recovery of rotationally symmetric beams", Applied Optics, Vol. 41, No. 26, 5512 – 5518, ISSN 0003-6935 (2002)
- K.-H. Brenner, P. Kümmel, U. Krackhardt: "Wellenoptische Optimierung des Schreib-/Lesekopfes für die hochdichte optische Speicherung", Simulation in Physik, Informatik und Informationstechnik (SYSI), 43 – 48, ISSN 0944-7121, 66. Physikertagung, Leipzig (2002)
- X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, "Reconstruction of two-dimensional complex amplitudes from intensity measurements", IOG 2002, Proceedings 1st Workshop Information Optics, 67 – 73, ISSN 1684-7296, Mannheim (2002)
- K.-H. Brenner, "Three dimensional Micro-integration of optical systems", 274. WE-Heraeus-Seminar on Microoptics, Bad Honnef, 22.-24.04.2002
- Ulrich Ehrbächer, Karl-Heinz Brenner, "Theoretical and experimental investigation of collimation properties of microlenses", 274. WE-Heraeus-Seminar on Microoptics, Bad Honnef, 22.-24.04.2002
- J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, "Realisierung abbildender Mikrooptiken durch Ionenaustauschtechniken in Glas", Buchbeitrag in Handbuch Mikrotechnik, Herausgeber Wolfgang Ehrfeld, Carl Hanser Verlag München, ISBN 3-446-21506-9, 347 – 406 (2002)
- X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, "Reconstruction of two-dimensional complex amplitudes from intensity measurements", Optics Communications 225, p. 19 - 30, (2003)
- W. T. Rhodes, K. -H. Brenner, and J. T. Sheridan, "Why teach Wigner Optics?," in Education and Training in Optics and Photonics, OSA Technical Digest Series (Optical Society of America), paper ETuB3, (2003)
- K. -H. Brenner, J. T. Sheridan, and W. T. Rhodes, "Teaching Wigner optics: what and how," in Education and Training in Optics and Photonics, OSA Technical Digest Series (Optical Society of America, 2003), paper EMI12.
- INVITED: Jochen Bähr, Karl-Heinz Brenner, "Applications and potential of the mask structured ion exchange techniques (MSI) in micro-optics", Proceedings of SPIE – Gradient Index, Miniature, and Diffractive Optical Systems III – Ed.: Thomas J. Suleski, Vol. 5177, p. 121 – 132 (2003)
- Jürgen Jahns, Karl-Heinz Brenner, Buchveröffentlichung: "Microoptics – From Technology to Applications", Optical Sciences, Springer Verlag New York / USA, ISBN 0387-20980-8 (2004)
- U. Ehrbächer, K.-H. Brenner, "Optimierung der Freistrahlübertragung in der Mikrooptik", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift d. DGaO), ISSN: 1614-8436, , 105. Jahrestagung in Bad Kreuznach (2004)
- S. Ziolkowski, K.-H. Brenner, "Spotformung für die optische Speicherung", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift d. DGaO), ISSN: 1614-8436, , 105. Jahrestagung in Bad Kreuznach (2004)
- INVITED: Karl-Heinz Brenner, "Optical Interconnects – Status and Future Developments", Nanofair 2004, International Symposium Karlsruhe, 23.-24. November 2004, VDI-Berichte Nr. 1839, p. 55 – 58, ISSN 0083-5560 (2004)
- X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, M. Wilzbach, M. Schwarz, T. Fernholz, and J. Schmiedmayer, "Fabrication of alignment structures for a fiber resonator by use of deep-ultraviolet lithography”, Appl. Opt. 44, No. 32, pp. 6857-6860 (2005)
- S. Ziolkowski, K.-H. Brenner, "Vectorial analysis and optimisation of ideal focusing lenses", EOS Topical Meeting On Advanced Optical Imaging Techniques, 29.06.-01.07.2005, London, p. 91-92, ISBN 3-00-016360-3 (2005)
- X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, C. Hruscha, "Efficient reconstruction of two-dimensional complex amplitudes using the Ambiguity function of one-dimensional slices", EOS Topical Meeting On Advanced Optical Imaging Techniques, 29.06.-01.07.2005, London, p. 40-41, ISBN 3-00-016360-3 (2005)
- K.-H. Brenner, X. Liu, "New description of the inhomogeneous wave for plane wave expansion in absorbing media", EOS Topical Meeting On Advanced Optical Imaging Techniques, 29.06.-01.07.2005, London, ISBN 3-00-016361-1 (2005)
- Dennis Dietrich, Karl-Heinz Brenner, Jochen Bähr, "Refractive beam shaping element fabricated by silver-sodium ion-exchange in glass", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, , 106. Jahrestagung in Breslau/Polen (2005)
- K.-H. Brenner, "Fabrication of asymmetric laser beam shaping elements", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, , 106. Jahrestagung in Breslau/Polen (2005)
- D. Wohlfeld, K.-H. Brenner, "Fabrication of integrated structures for coupling VCSEL to fibre", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 106. Jahrestagung in Breslau/Polen (2005)
- S. Ziolkowski, K.-H. Brenner, "Polarisation properties of a perfect high-NA focusing lens", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, , 106. Jahrestagung in Breslau/Polen (2005)
- A. Haase, M. Schwarz, M. Wilzbach, J. Schmiedmayer, X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, B. Hessmo, P. Horak, “Microcavities on atom chips for single-atom detection”, Quantum Electronics Conference, 2005. EQEC '05. European Publication Date: 12-17 June 2005, p. 354 (2005)
- D. Wohlfeld, K.-H. Brenner, "Fabrikation und Integration von mechanisch-optischen Strukturen zur Kopplung von VCSELs mit Glasfasern, Mikrosystemtechnik Kongress 2005, ISBN 978-3-8007-2926-5 / ISBN 3.8007-2926-1, pp 167-169, http://www.gsi.de/documents/DOC-2007-Jul-4.html;, (2005)
- B. Trauter, K.-H. Brenner, "Anwendung des optimierten Phasenkontrastverfahrens für die opische Vermittlungstechnik", ORT 2005, 8. Workshop Optik in der Rechentechnik, ISSN 1437-8507, p. 70-75, Ilmenau (2005)
- D. Wohlfeld, K.-H. Brenner, "Anwendung optischer Verbindungstechniken in der Hochenergiephysik", ORT 2005, 8. Workshop Optik in der Rechentechnik, ISSN 1437-8507, p. 76-82, Ilmenau (2005)
- Brenner, K.-H., "Entwurf und Realisierung von Freiform-Mikrooptiken für die Strahlformung", Innovation Optischer Systeme II, 21. Optik-Kolloquium/ITO, Stuttgart-Vaihingen, 22.02.2006
- K.-H. Brenner, Lars Lehmann, "Treatment of finite diameter beams in multilayered media using the plane wave decompostion", EOS Topical Meeting on Molecular Plasmonic Devices, ISBN-10: 3-00-018607-7, pp. 96 – 98, Engelberg (CH), 27.-29.04.2006
- David L. Shealy, John A. Hoffnagle, and Karl-Heinz Brenner "Analytic beam shaping for flattened output irradiance profile", SPIE Proceedings, Vol. 6290, No. 01, Annual Meeting of SPIE, Laser Beam Shaping VII Conference, San Diego, 13.–14. 08. 2006
- B. Trauter, K.-H. Brenner, "Anwendung des Phasenkontrastverfahrens in der optischen Übermittlungstechnik", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, , 107. Jahrestagung in Weingarten (2006)
- S. Ziolkowski, K.-H. Brenner, "Numerische Methoden zur Bestimmung der Einkopplungseffizienz in Multimode-Wellenleitern", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 107. Jahrestagung in Weingarten (2006)
- D. Wohlfeld, S. Scheffelmeier, K.-H. Brenner, "Doppelbelichtung und Replikation von Mikrostrukturen für die optische Informationsverarbeitung", DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 107. Jahrestagung in Weingarten (2006)
- Xiyuan Liu, K.-H. Brenner, „Effiziente numerische Behandlung teilkohärenter Lichtausbreitung“, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, , 107. Jahrestagung in Weingarten (2006)
- Karl-Heinz Brenner, Lars Lehmann, „Treatment of Spatially Variing Filds in Multilayered Media Using the Plane Wave“, ICO Topical Meering on Optoinformatics/Information Photonics, St. Petersburg/Russland (2006)
- Xiyuan Liu, Christian Hruscha, Karl-Heinz Brenner, „Efficient Reconstruction of Two-Dimensional Complex Amplitudes Using the Ambiguity Function of One-Dimensional Slices“, ICO Topical Meering on Optoinformatics/Information Photonics, St. Petersburg/Russland (2006)
- Marco Wilzbach, Albrecht Haase, Michael Schwarz, Dennis Heine, Kai Wicker, Xiyuan Liu, Karl-Heinz Brenner, Sönke Groth, Thomas Fernholz, Björn Hessmo, Jörg Schmiedmayer, „Detecting neutral atoms on an atom chip“, Fortschr. Phys. 54, No. 8-10, pp. 746-764 (2006)
- Eike Slogsnat, Karl-Heinz Brenner, „Wellenoptische Analyse von Multimode-Wellenleitern Vergleich BPM/WPM“, ORT 2006, 9. Workshop Optik in der Rechentechnik, ISSN 1437-8507, p. 28 - 34, Siegen (2006)
- Denis Wohlfeld, Karl-Heinz Brenner, „UV-Tiefenlithographie mit Zweiphasenbelichtung zur Herstellung von replizierbaren optischen Verbindungsstrukuren“, ORT 2006, 9. Workshop Optik in der Rechentechnik, ISSN 1437-8507, p. 106 - 109, Siegen, http://www.gsi.de/documents/DOC-2007-Jul-7.html;, (2006)
- Marco Wilzbach, Albrecht Haase, Michael Schwarz, Dennis Heine, Kai Wicker, Xiyuan Liu, Karl-Heinz Brenner, Sönke Groth, Thomas Fernholz, Björn Hessmo, Jörg Schmiedmayer, „Detecting neutral atoms on an atom chip“, Elements of Quantum Information, eds. W. P. Schleich u. H. Walther, ISBN: 978-3-527-40725-5, pp 185 – 210 (2007)
- INVITED: Karl-Heinz Brenner, „Plane Wave Decomposition in Layered Materials and Meta-materials“, CP949, 6th International Workshop on Information Optics (WIO ’07), ed. J.A. Benediktsson, B. Javidi, K.S. Gudmundsson, American Institute of Physics (AIP), ISBN 978-0-7354-0463-2/07, pp 59 – 66, Reykjavik/Island, (2007)
- INVITED: K. -H. Brenner, “Optical Communication and Switch Technology“,http://www.supercomp.de/isc2007, 22. International Supercomputing Conference (ISC) in Dresden (2007)
- Xiyuan Liu, Christian Hruscha, and Karl-Heinz Brenner, „Efficient reconstruction of two dimensional complex amplitudes utilizing the redundancy of the ambiguity function“, Appl. Opt. 47, No. 22, pp E1 – E7 (2008)
- Xiyuan Liu and Karl-Heinz Brenner, “Minimal optical decomposition of ray transfer matrics, Appl. Opt. 47, No. 22, pp E88 – E98 (2008)
- Andreas Unger, Karl-Heinz Brenner, “Vergleich exakter optischer Lösungsmethoden im Zeitbereich in Hinblick auf Genauigkeit und Effizienz”, DGaO-Proceedings 2008, http://www.dgao-proceedings.de/;, ISSN 1614-8436, 109. Jahrestagung in Esslingen am Neckar/Deutschland (2008)
- Bastian Trauter, Karl-Heinz Brenner, “Schnelle Profilformbestimmung von diffraktiven Elementen durch Least-Square-Approximation mit verschobenen Basisfunktionen”, DGaO-Proceedings 2008, http://www.dgao-proceedings.de/;, ISSN 1614-8436, 109. Jahrestagung in Esslingen am Neckar/Deutschland (2008)
- Ulrike Maier, Jens Hoffmann, Karl-Heinz Brenner, “Surface Reconstruction from gradient data”, DGaO-Proceedings 2008, http://www.dgao-proceedings.de/;, ISSN 1614-8436, 109. Jahrestagung in Esslingen am Neckar/Deutschland (2008)
- E. Slogsnat, K.-H. Brenner, P. Ehrle, W. Stumpfs, “Selbstkonsistentes iteratives Verfahren zur Bestimmung glatter Oberflächen“, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 109. Jahrestagung in Esslingen am Neckar/Deutschland (2008)
- INVITED: Karl-Heinz Brenner “Shifted Base Functions: An Efficient and Versatile New Tool in Optics”, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 139 012002, 11 pp, ISSN 1742-6588, Workshop on Information Optics (WIO’08), 01.-05.06.08 in Annecy (2008)
- B. Trauter, J. Hetzler, K.-H. Brenner, "Analysis of the uniqueness of an inverse grating characterization method", Optics+Photonics, 12.-14.8.2008, San Diego, USA, Proceedings of the SPIE, Vol. 7065 (2008)
- B. Trauter, J. Hetzler, K.-H. Brenner, "Inverse method for the characterization of two-dimensional diffraction gratings", 14th Microoptics Conference, 25.-27.9., Brussels, Belgium, Technical Digest, pp 131 – 132 (2008)
- Xiyuan Liu, Karl-Heinz Brenner, “Tiefenlithographie zum Spleißen von Singlemodefasern”, Photonik, 40. Jahrgang, No. 5, pp. 52-54 (2008)
- N. Moll, T. Morf, M. Fertig, T. Stöferle, B. Trauter, R.F. Mahrt, J. Weiss, T. Pflüger, and K.-H. Brenner „Polarization-Independent Photo- Detectors with Enhanced Responsivity in a Standard SOI CMOS Process“, IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology, Vol. 27, No. 21, 4892-4896, (2009))
- F. Merchán, D.Wohlfeld, K.-H. Brenner, “ Development of active optical cables“, Workshop of Optics in Computing (Optik in der Rechentechnik, ORT), Proceedings of the Workshop Optics in Computing 2009, ISBN 978-3-200-01636-1, pp 45 – 47, Wien (2009)
- E. Slogsnat, K.-H. Brenner, “Non-stereoscopic method for deflectometric measurement of reflecting surfaces“, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 110. Jahrestagung in Brescia/Italien, (2009)
- D. Wohlfeld, E. Slogsnat, K.-H. Brenner, “Integrated beam splitters for array microscopy in life science“, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 110. Jahrestagung in Brescia/Italien, (2009)
- F. Merchán, D. Wohlfeld, K.-H. Brenner, “High speed communication using micro optical integration“, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 110. Jahrestagung in Brescia/Italien, (2009)
- M. Auer, K.-H. Brenner, “Treatment of spatially varying Permeabilities with the RCWA-Application to Negative-Index Materials“, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 110. Jahrestagung in Brescia/Italien, (2009)
- Xiyuan Liu, Karl-Heinz Brenner, “Guide structures for splicing single-mode fibres fabricated using deep lithography”, Photonik international 2009/2, pp. 42-43, (2009)
- F. Merchán, D. Wohlfeld, K.-H. Brenner, “Micro integration of optical systems for the fabrication of active optical cables“, 3rd EOS Topical Meeting on Optical Microsystems (OMS09), ISBN 978-3-00-024191-8, (2286), 27.-30.09.09.Capri/Italien (2009).
2010-2018
Details
- INVITED: Karl-Heinz Brenner ,“General Solution Of Two-Dimensional Beam-Shaping With Two Surfaces”, 8. International Workshop on Information Optics (WIO’09), 20.-24.06.09 in Paris / France , Journal of Physics (IOP): Conference Series, Vol. 206 (012021), doi # 10.1088/1742-6596/206/1/012021, ISSN 1742-6596, http://iopscience.iop.org/1742-6596/206/1/012021/, ISSN 1742-6588 (print), (2010)
- M. Fertig, K.-H. Brenner, “The Vector wave propagation method (VWPM)”, JOSA A, Vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 709 – 717, (2010)
- M. Auer, K.-H. Brenner, N. Moll, T. Morf, M. Fertig, T. Stöferle, R.F. Mahrt, J. Weiss, T. Pflüger, „Enhancement of Photo-Detector Responsivity in Standard SOI CMOS Processes by introdurcing Resonant Grating Structures“, EOS Topical Meeting on Diffractive Optics, 14.-18.02.2010, Koli/Finnland, ISBN 978-3-00-024193-2, (2010)
- K.-H. Brenner, “General Solution Of Two-Dimensional Beam-Shaping With Two Surfaces”, Advances in Information Optics and Photonics, Springer Verlag, Part 1, pp. 3-11. DOI: 10.1007/987-1-4419-7380-1_1, (2010)
- F. Merchán, D. Wohlfeld, K.-H. Brenner, “Micro integration of optical components for the fabrication of active optical cables”, Journal of the European Optical Society - Rapid Publications, Vol. 5, Pub.nr. 10056 (2010)
- F. Merchán, Karl Heinz Brenner, Peter Gregorius, Sven Hendrik Voß, “FPGA-Board and Active Optical Cable Design for Multi-Gigabit Communication”, ESTC 2010 (Electronics System Integration Technology Conferences), Digital Proceedings, poster session 1, Prod# CFP10TEM-POD, ISBN 9781424485536, P#0032, pp882 (2010)
- F. Merchan, X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, “Effiziente Faserkopplung mit Gradientenindex-Stablinsen”, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 111. Jahrestagung in Wetzlar, (2010)
- E. Slogsnat, R. Buschlinger, K.-H. Brenner, “Miniaturisierte parallele Mikroskopie in der Systembiologie”, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436, 111. Jahrestagung in Wetzlar, (2010)
- F. Merchán, K.-H. Brenner, R. Börret, U. Berger, „Cost optimized fabrication of Micro-Optical Couplers“, Optical Fabrication and Testing (OF&T), OSA, Technical Digest, ISBN 978-1-55752-893-3, 13.-16-06.2010, Jackson Hole, Wyoming, USA, (2010)
- Karl-Heinz Brenner, „Aspects for calculating local absorption with the rigorous couple-waved method“, Optics Express, Vol. 18, Iss. 10, pp. 10369-10376, (2010)
- R. Buschlinger, K.-H. Brenner, „Light Focusing by binary phase gratings“, 5th EOS Topical Meeting on Advanced Techniques (AIT), ISBN 978-3-00-030503-0, 29.06.-02.07.2010, Engelberg/Ch
- M. Auer, K.-H. Brenner, „Enhancement of Photodetector Responsivity in Standard SOI CMOS Processes by introducing Resonant Grating Structures”, JEOS:RP 6, 110145 (2011)
- INVITED: Karl-Heinz Brenner, Robert Buschlinger, “Fractal diffraction and focusing properties of binary phase gratings”, 9. Euro-American Workshop on Information Optics (WIO 2010), IEEE, ISBN 978-1-4244-8227-6/10, 12.-16. Juli 2010, Helsinki / Finnland, (2010)
- F. Merchán, K.-H. Brenner, "A concept for the assembly and alignment of arrayed microelectronic and micro-optical systems for Optical Multi-Gigabit Communication", Optoelectronic Interconnects and Component Integration XI Conference OE112, 22.-27.01.2011, San Francisco, California, USA, Proc. of SPIE Vol. 7944, 49440D, (2011)
- K.-H. Brenner, R. Buschlinger, „Parallel image scanning with binary phase gratings“, Journal of European Optical Society : Rapid Publications 6, 11024 (JEOS:RP), ISSN 1990-2573, (2011)
- F. Merchán, K.-H. Brenner, P. Gregorius, S.-H. Voß, „FPGA-Board and Active Optical Cable Design für optische Multi-Gigabit Übertragung“, PLUS 12 / 2010 (Produktion von Leiterplatten und Systemen / Fachzeitschrift für Aufbau u. Verbindungstechnik in der Elektronik, Leuze Verlag), Band 12, ISSN 1436-7505 B 49475, pp. 2800-2809, (2010)
- K.-H. Brenner, “ Aspekte der Lichtausbreitung zwischen verkippten Ebenen ”, DGaO-Proceedings (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2011-B009-2, 112. Jahrestagung, 14.-18. Juni 2011, Ilmenau, (2011)
- F. Merchàn, K.-H. Brenner, „Monolithisches Fertigungskonzept für die kostengünstige Herstellung optischer Mikrosysteme“, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2011-B004-0, 112. Jahrestagung, 14.-18. Juni 2011, Ilmenau, (2011)
- T. Stenau, X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, „Analyse eines neuen Systemkonzepts zur parallel scannenden Mikroskopie“, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2011-P005-9, 112. Jahrestagung, 14.-18. Juni 2011, Ilmenau, (2011)
- E. Slogsnat, K.-H. Brenner, „ Design des Beleuchtungspfads für ein miniaturisiertes paralleles Fluoreszenz-Mikroskop“, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2011-P00x-x, 112. Jahrestagung, 14.-18. Juni 2011, Ilmenau, (2011)
- INVITED: K.-H. Brenner, „Parallel non-mechanical image scanning with micro lenses and binary phase gratings!, 10th Euro-American Workshop on Information Optics (WIO 2011), 20.-24. Juni 2011, Benicassim / Spanien, (2011)
- INVITED: D. Wohlfeld, K.H. Brenner, “Aspects of short-range interconnect packaging”, SPIE Photonics West Conference / Optoelectronic Interconnects XII, 8267-26, 24.-26.01.2012, San Francisco, USA (2012)
- M. Auer, K.-H. Brenner, “Calculation of Local Absorption in
three-dimensional Structures using RCWA”, 8th EOS Topical Meeting on Diffractive Optics, 27.02.-01.03.2012, ISBN 978-3-00-033711-6, Delft/NL, (2012)
- K.-H. Brenner, “Optimization of local absorption in layered media”, 8th EOS Topical Meeting on Diffractive Optics, 27.02.-01.03.2012, ISBN 978-3-00-033711-6, Delft/NL, (2012)
- F. Merchàn, K.-H. Brenner, „Novel integrated micro-optics system for the fabrication of Active Optical Cables“, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2012-B036-5, 113. Jahrestagung, 29. Mai-02. Juni 2012, Eindhoven, (2012)
- E. Slogsnat, L. Lehmann, P. Fischer, K.-H. Brenner, “Concept and Implementation of a Compact Multi-Channel Fluorescence-Microscope Unit”, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2012-P002-9, 113. Jahrestagung, 29. Mai-02. Juni 2012, Eindhoven, (2012)
- K.-H. Brenner, R. Buschlinger, “Talbot Focusing – a new effect of periodic structures and ists utilization”, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2012-P040-7 113. Jahrestagung, 29. Mai-02. Juni 2012, Eindhoven, (2012)
- INVITED: K.-H. Brenner, X. Liu, „High resolution wavefriont sensing with non-interferometric techniques”, 11th Euro-American Workshop on Information Optics (WIO 2012), IEEE, DOI 101109/WIO.2012.6488919, 20.-24. August 2012, Quebec, Kanada (2012)
- X. Liu, T. Stenau and K.-H. Brenner „Diffractive micro lens arrays with overlapping apertures”, 11th Euro-American Workshop on Information Optics (WIO 2012), IEEE, DOI 101109/WIO.2012.6488929, 20.-24. August 2012, Quebec, Kanada (2012)
- K.-H. Brenner and X. Liu "Phase retrieval from multi-plane intensity measurements with wavefront sensing", Digital Holography and 3D Imaging, 21.-25. April 2013, ISBN: 978-1-55752-964-0, http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/DH.2013.DTh4A.8, Hawaii, USA (2013)
- T. Stenau, K.-H. Brenner, “Analyse der Designparameter von binären diffraktiven Mikrolinsenarrays in Hinblick auf den Herstellungsprozess”, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2013-P051-0 114. Jahrestagung, 21.-25. Mai 2013, Braunschweig, (2013)
- X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, “Iterative Phasenrekonstruktion mit einem diffraktiven Element”, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2013-B001-5 114. Jahrestagung, 21.-25. Mai 2013, Braunschweig, (2013)
- K.-H. Brenner, T. Stenau, M. Azizian,“ Entwicklung eines scannenden Mikroskops mit diffraktiven Mikrolinsen ”, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2013-B024-6 114. Jahrestagung, 21.-25. Mai 2013, Braunschweig, (2013)
- X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, „High resolution wavefront measurement with phase retrieval using a diffractive overlapping micro lens array“, 7th International Workshop on Advanced Optical Imaging & Metrology (Fringe 2013), pp 233-236, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-36359-7_35, ISBN 978-3-642-36358-0, ed. W. Osten, 08.-11.09.2013, Nürtingen, (2013)
- A. Junker, Tim Stenau, K.-H. Brenner, „Wave optical reconstruction of plenoptic camera images“, 7th International Workshop on Advanced Optical Imaging & Metrology (Fringe 2013), pp 117-122, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-36359-7_14, ISBN 978-3-642-36358-0. ed. W. Osten, 08.-11.09.2013, Nürtingen, (2013)
- X. Liu, K-H. Brenner, "Phase Retrieval with a Diffractive Micro Lens Array", International Journal of Optomechatronics, Taylor & Francis, Vol. 8, Issue 4, pp 251-259, ISSN: 1559-9612 print / 1559-9620 online, DOI: 10.1080/15599612.2014.942956 (2014)
- A. Junker, T. Stenau, K.-H. Brenner, "Scalar wave-optical reconstruction of plenoptic camera images", Applied Optics 53, No. 25, 5784-5790, (2014)
- M. Auer, K.-H. Brenner, “Localized input fields in rigorous coupled-wave analysis”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 31, No. 11, (2014)
- T. Paul, K.-H. Brenner, "Unersuchung und Anwendung von Schmelzlackstrukturen in der Mikrooptik", (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2014-P034-8, 115. Jahrestag, 10.-14. Juni 2014. Karlsruhe, (2014)
- K.-H. Brenner, M. Auer, “Lokalität von Quellen und Senken in der exakten optischen Simulation”, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2014-H004-1 115. Jahrestagung, 10.-14. Juni 2014, Karlsruhe, (2014)
-
X. Liu, K.-H. Brenner, “Einfluss der Kamera-Auflösung auf die spatiale Auflösung von Phase Retrieval”, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2014-A012-3, 115. Jahrestagung, 10.-14. Juni 2014, Karlsruhe, (2014)
-
A. Junker, K.H. Brenner, "Simulation and Analysis of SNOM Measurements using Rigorous Coupled-Wave Analysis", (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für amgewandte Optik e.V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2015-A019-6, 116. Jahrestagung, 26.-29. Mai 2015, Brno/Czech Republic, (2015)
-
A. Junker, K.-H. Brenner, "Structuring the incident and transmitted regions in rigorous coupled-wave analysis", 15th Workshop on Information Optics (WIO), IEEE, 978-1-5090-2163-5/16, 11.-15- Juli 2016, Barcelona, Spanien, (2016)
-
INVITED: K.-H. Brenner, M. Auer, "Verification of Near-field Calculations by Conversation Laws", 15th Workshop on Information Optics (WIO), IEEE, 978-1-5090-2163-5/16, 11.-15. Juli 2016, Barcelona, Spanien, (2016)
-
T. Stenau, K.-H. Brenner, “Light concentration efficiency of diffractive lenses with overlapping apertures”, (Online-Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft für angewandte Optik e. V.), ISSN: 1614-8436-urn:nbn:de:0287-2016-C017-5, 117. Jahrestagung, 17.-21. Mai 2016, Hannover, (2016)
-
T. Stenau, K.-H. Brenner, „Diffractive Lenses with Overlapping Aperture – A New Tool in Scanning Microscopy“, Proceedings Imaging and Applied Optics - Imaging Systems and Applications, Optical Society of America 2016, IT1F-1, ISBN: 978-1-9433580-15-6, https://doi.org/10.1364/ISA.2016.IT1F.1, 25.-28. Juli 2016, Heidelberg, (2016)
-
K.-H. Brenner, S. Mehrabkhani, „Modification of Spatial Domain Algorithms for Apertureless Light Propagation“, Applied Optics 56, No. 1, A8 – A12, Doc.ID 273329, (2017)
-
A. Junker, K.-H. Brenner, “Two-sided illumination in rigorous coupled-wave analysis applied to the 4π-microscope”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, Vol. 34, No. 10, pp. 1769-1775, (2017)
-
INVITED: K.-H. Brenner, “A high-speed version of the wave propagation method applied to micro-optics”, 16th Workshop on Information Optics (WIO), IEEE Xplore Digital Libary, 03.-07. Juli 2017, Interlaken, Schweiz, (2017)
-
A. Junker, K.-H. Brenner, „Bidirectional light incidence in rigorous coupled-wave analysis applied to 4 π-microscopy“, 16th Workshop on Information Optics (WIO), IEEE Xplore Digital Libary, 03.-07- Juli 2017, Interlaken, Schweiz, (2017)
-
A. Junker, K.-H. Brenner, „High mode count rigorous simulation of diffractive optical elements by an iterative solution approach“, EOS Topical Meeting on Diffractive Optics (DO), ISBN 978-952-68553-4-9, 04.-07-September 2017, Joensuu, Finnland, (2017)
-
A. Junker, K.-H. Brenner, “Achieving a high mode count in the exact electromagnetic simulation of diffractive optical elements”, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, Vol. 35, No. 3, 377-385, (2018)
|
Patents:
| |
|
P1-1
|
A. Lohmann, K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Shuffle Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 17.06.1986, Patentnummer: EP 0 229 177 B1
|
|
P1-2
|
A. Lohmann, K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optische Umordnungsanordnung Anmeldetag: 17.06.1986, Patentnummer: DE 3686710 T2
|
|
P1-3
|
A. Lohmann, K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Shuffle Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 17.06.1986, Patentnummer: WO 87/00314
|
|
P1-4
|
A. Lohmann, K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Shuffle Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 23.06.1986, Patentnummer: CA000001295498C
|
|
P2-1
|
K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Spatial Logic Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 14.07.1986, Patentnummer: US 4,842,370
|
|
P2-2
|
K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Spatial Logic Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 06.07.1987, Patentnummer: EP 0 253544 B1
|
|
P2-3
|
K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Räumliche, optische logische Anordnung Anmeldetag: 13.07.1987, Patentnummer: DE 3750 645 T2
|
|
P2-4
|
K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Spatial Logic Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 13.07.1987, Patentnummer: CA000001281138C
|
|
P1-5
|
A. Lohmann, K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Shuffle Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 11.01.1989, Patentnummer: US 4,931,959
|
|
P3
|
H. Wolf, J. Bähr, K.-H. Brenner, „Projektionsverfahren und Projektor“, Anmeldetag: 05.10.1994, Patentnummer: DE 195 02 660 C2
|
|
P2-5
|
K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Spatial Logic Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 24.02.1995, Patentnummer: SG000009590335A2
|
|
P2-6
|
K.-H. Brenner, A. Huang, „Optical Spatial Logic Arrangement“, Anmeldetag: 31.08.1995, Patentnummer: HK000000136595A
|
|
P4
|
U. Krackhardt, K.-H. Brenner, „Absolutes, flächenhaftes Interferometer“, Anmeldetag: 24.07.1998, Patentnummer: DE 198 33 291 A1
|
|
P5-1
|
K.-H. Brenner, „Element zur kombinierten Symmetriesierung und Homongenisierung eines Strahlenbündels“, Anmeldetag: 04.05.2001, Patentnummer: DE 101 21747 B4
|
|
P5-2
|
K.-H. Brenner, „Element for the combined symmetrization and homogenization of a bundle beams”, Anmeldetag: 19.03.2002, Patentnummer: WO 02/086592
|
|
P5-3
|
K.-H. Brenner, „ Element zur kombinierten Symmetriesierung und Homongenisierung eines Strahlenbündels”, Anmeldetag: 19.03.2002, Patentnummer: EP 1 370 896 B
|
|
P5-4
|
K.-H. Brenner, „Element for the combined symmetrization and homogenization of a bundle beams”, Anmeldetag: 19.03.2002, Patentnummer: US 7,298, 553 B2
|
|
P5-5
|
K.-H. Brenner, „Element for the combined symmetrization and homogenization of a bundle beams”, Anmeldetag: 20.08.2003, Patentnummer: KR 1020030097805 A
|
|
P6-1
|
K.-H. Brenner, U. Brüning, „Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung einer optischen Verbindung zwischen einem optoelektronischen Bauteil und einem Lichtwellenleiter”, Anmeldetag: 07.08.2004, Patentnummer: DE 10 2004 038 530 B3
|
|
P6-2
|
K.-H. Brenner, U. Brüning, „Methods and device establishing an optical connection between an optoelectronic component and an optical waveguide”, Anmeldetag: 08.08.2005, Patentnummer: US 7,218,804 B2
|
|
P7
|
D. Wohlfeld, K.-H. Brenner, U. Brüning, „Über optische Verbinder und dessen Herstellung“, UHD07a, DE 10 20120 018 248.6, angemeldet
|
|
P8
|
K.-H. Brenner, „Vorrichtung und Verfahren zur Strahlungskonzentration mit einem Phasengitter“, Anmeldung beim Europäischen Patentamt in München, 05.10.2010, Az: PCT/EP2010/006070, internationale Veröffentlichungsnr. WO 2012/045318 A1, 12.04.2012 (2010)
|
|
Dissertations:
| |
- J. Schulze: „Entwicklung von Mikrolinsenfeldern und kompakten optischen Schnittstellen für die optische Hybridtechnik“, (2001).
- Róbert Klug: „Entwurf und Aufbau mikro-optischer Systeme für die Mess- und Übertragungstechnik“, (2002).
- X. Liu: „Design, analysis and fabrication of micro optical systems involving uv-deep lithography –with an Application in Atomic Physic“, (2008).
- B. Trauter: „Untersuchungen zum inversen, elektromagnetischen Gitterbeugungsproblem mit Anwendungen in den Gittercharakterisierung “,(2008).
- D. Wohlfeld: „ Simulation, analysis, and fabrication of miniaturized components with applications in optical interconnects and parallel microscopy “, (2009).
- A. Unger: “Refractive index sensing with localized plasmonic resonances – Theoretical description and experimental verification”, (2010).
- M. Fertig: „Vector Wave Propagation Method”, (2011).
- F. Merchán: „Untersuchungen zur Mikrointegration optischer Übertragungssysteme im Kurzstreckenbereich“, (2012).
- E. Slogsnat: „Aspects and implementations for accelerating image acquisition in microscopy“, (2013).
- M. Auer: „Numerical treatment of localized fields in rigorous diffraction therory and its application to light absorption in structured layers“, (2016).
- T. Stenau: „ Diffraktive Linsen mit überlappenden Apperturen in Simulation und Anwendung“, (2017)
- A.Junker: „Advances in the performance and applicability of Modal Electromagnetic Simulations“, (2018)
|
Diploma, Bachelor and Master Theses:
| |
Master Theses
- André Junker: „Wave-optical Reconstruction of Plenoptic Camera Images“, (2013)
- Torsten Paul: „Entwicklung, Herstellung und Analyse von refraktiven Mikrostrukturen“, (2014)
- Rico Erhard: „Transformed diffraction gratings, designs and simulations“, (2017)
Bachelor Theses
- Phuong Vu Nguyen: „Untersuchung zur Eignung des Android-Betriebssystems für wissenschaftliche Software“, (2014)
- Janis Postels: „Untersuchung der Anwendbarkeit der Transport-of-Intensity-Equation zur Phasenrekonstruktion“, (2016)
- Habib Gahbiche: „Array von diffraktiven optischen Elementen zur Erzeugung ringförmiger Foki und Ortsbestimmung“, (2016)
- Julian Albus: „Phasenrekonstruktion mithilfe von Phasenmodulation“, (2017)
Diploma Theses
- Sven Flammuth: „Mikrointegration optischer Module für die faseroptische Übertragung nach dem Winkelmultiplex-Verfahren“, (2002)
- Xiyuan Liu: „Rekonstruktion von Signalphasen mit der Ambiguity Funktion“, (2002)
- Hannes Lippet: „Implementierung und Evaluation von Interpolationsalgorithmen für die Behandlung optischer Freiformflächen“, (2004)
- Denis Wohlfeld: „Untersuchung zur Herstellung von Mikroprismen für die optische Verbindungstechnik“, (2004)
- Christian Hruscha: „Phasenrekonstruktion aus Intensitätsmessungen“, (2005)
- Johannes Holzer: „Algorithmen zur Phasenkontinuierung in der optischen Interferometrie“, (2005) Dennis Dietrich: „Modellierung und numerische Simulation des feldunterstützten Ionenaustauschs in Glas“, (2005)
- Bastian Trauter: „Optimierung des Phasenkontrastverfahrens für die optische Lichtablenkung“, (2005) Matthias Lang: „Untersuchungen von Schaltungsentwicklungen für einen Sensor zur Messung von Lichtlaufzeit“, (2005)
- Sven Scheffelmeier: „Untersuchung von Verfahren zur Replikation mikrooptischer Elemente“, (2006)
- Lars Lehmann: „Modellierung und Simulation von leitfähigen Mehrschichtsystemen“, (2006)
- Eike Slogsnat: „Entwurf u. Charakterisierung von optischen Mikrostrukturen für die Taktverteilung in integrierten Schaltkreisen“, (2006)
- Philip Ehrle: „Optimierung reflektierender Freiformflächen zur optischen Strahlformung“, (2007)
- Jens Hoffmann: „Entwurf und Aufbau eines adaptiven Wellenfrontsensors“, (2008)
- Hanna Jödicke: „Untersuchung von 3D-Nanostrukturen mit rigorosen Beugungsmethoden“, (2008)
- Emanuel Gores: „Anwendung von Least-Square-Verfahren für die Optimierung von Freiformflächen“, (2008)
- Max Auer: „Numerische Analyse optischer Nanostrukturen mit dreidimensionalen rigorosen Methoden“, (2009)
- Jan Gumprecht: „Development and Validation of an Opten-Source Freehand 3D Ultrasound Navigation System for Liver Surgery with GPGPU Acceleration“, (2009)
- Robert Buschlinger: „Untersuchungen zur miniaturisierten Mikroskopie für die Systembiologie“, (2010)
- Eva K. Treiber: „Ausarbeitung und Implementierung einer Finite-Differenzen-Methode zur Berechnung der Lichtausbreitung im Zeitbereich“, (2012)
- Tim Stenau: „Theoretische, numerische und experimentelle Untersuchung eines neuen Ansatzes zur parallel scannenden Mikroskopie“, (2012)
- Armin Weyer: „Untersuchung zur Erhöhung der Genauigkeit eines Hartmann-Shack-Sensors mit diffraktiven Linsen“, (2015)
|
Download Reports
The following annual reports, covering the period from 1997-2017, are published under ISSN 2197 - 4462.












